Emulsi VAE merupakan produk ramah lingkungan. Gugus vinil tertanam dalam rantai molekul polivinil asetat, sehingga emulsi polimer ini memiliki suhu pembentukan film yang rendah dan sifat pembentukan film yang sangat baik. Emulsi ini memiliki daya rekat yang kuat pada material yang sulit direkatkan seperti PET, PVC, PE, dan PP. Film polimer yang dihasilkan sangat tahan air dan cuaca. Emulsi ini juga tahan terhadap penggosokan dan tetap fleksibel bahkan pada suhu rendah. Ketebalan emulsi VAE dipengaruhi oleh beberapa faktor.
1. Pengaruh Kandungan Padatan terhadap Viskositas
Kami melakukan pengujian ekstensif pada formulasi dan kondisi proses Emulsi VAE DA-180L Dan VINNAPAS 400, masing-masing. Data dalam tabel berikut berasal dari pengujian ini. Hubungan antara kandungan padatan dan viskositas ditunjukkan pada Tabel 1.
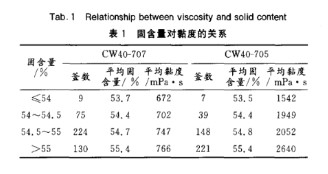
Seperti ditunjukkan pada Tabel 1, kandungan padatan yang lebih tinggi meningkatkan viskositas. Hal ini disebabkan oleh peningkatan kandungan padatan yang meningkatkan jumlah partikel koloid dalam massa emulsi yang sama, mengurangi jumlah fase air, dan meningkatkan luas permukaan total partikel. Hal ini meningkatkan interaksi antarpartikel dan resistensi terhadap gerakan, sehingga menghasilkan viskositas yang lebih tinggi.
2. Pengaruh Koloid Pelindung terhadap Viskositas
Dalam polimerisasi emulsi, koloid pelindung sering digunakan sebagai penstabil emulsi untuk meningkatkan stabilitas pengemulsi dan menyesuaikan viskositas. Stabilitas emulsi PVA yang terhidrolisis sebagian juga terkait dengan distribusi gugus asetil pada rantai polimer. Tingkat kegumpalan yang lebih tinggi dalam distribusi gugus asetil menghasilkan aktivitas permukaan yang lebih besar, stabilitas emulsi yang lebih baik, dan emulsi yang lebih kecil dan lebih kental. Semakin tinggi derajat polimerisasi PVA, semakin tinggi viskositas larutan berair polivinil alkohol sebelum polimerisasi, dan semakin tinggi viskositas VAE. Semakin tinggi derajat alkoholisis PVA, semakin rendah viskositas VAE. Kemampuan koloid pelindung PVA meningkat dengan meningkatnya derajat polimerisasi. PVA derajat rendah membentuk partikel lateks yang lebih kasar dan memiliki viskositas yang lebih rendah. Peningkatan derajat polimerisasi meningkatkan kemampuan pelindung dan pendispersi. Untuk mempertahankan sifat dispersi dan protektif PVA selama polimerisasi emulsi, selain hanya menyesuaikan viskositas, jumlah total PVA biasanya dijaga konstan, hanya rasio antara keduanya yang disesuaikan. Dengan kondisi lain yang tidak berubah, penambahan 4,54 kg PVA Polivinil Alkohol 088-20 akan meningkatkan viskositas setiap batch sebesar 100 mPa·s. Tabel 2 mencantumkan berat molekul dan distribusi berat molekul emulsi VAE dengan viskositas tinggi dan rendah.
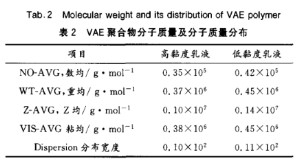
Tabel 2 menunjukkan bahwa emulsi viskositas rendah mempunyai berat molekul lebih tinggi, partikel lebih kasar, dan distribusi ukuran partikel lebih luas daripada emulsi viskositas tinggi, sehingga menghasilkan viskositas lebih rendah.
3. Pengaruh Inisiator Awal terhadap Viskositas
Inisiator memiliki pengaruh utama terhadap kecepatan polimerisasi. Semakin banyak inisiator yang digunakan, semakin cepat reaksi polimerisasi berlangsung, dan reaksi tersebut sulit dikontrol. Setelah kondisi polimerisasi dan jenis inisiator ditentukan, jumlah inisiator dapat digunakan untuk menyesuaikan berat molekul polimer. Semakin banyak inisiator yang digunakan, semakin kecil berat molekul polimer, dan viskositas emulsi meningkat, begitu pula sebaliknya. Di antara faktor-faktor tersebut, jumlah inisiator awal (ICAT) yang ditambahkan memiliki pengaruh terbesar.
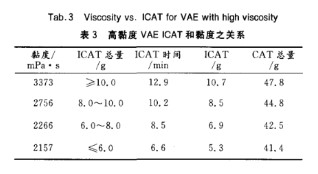
Data ini dengan jelas menunjukkan bahwa semakin banyak inisiator awal yang ditambahkan, semakin tinggi viskositas emulsi. Hal ini disebabkan oleh semakin banyak inisiator awal yang ditambahkan, semakin sulit monomer bereaksi atau laju reaksinya lambat pada tahap awal, sehingga polimer yang dihasilkan memiliki berat molekul yang lebih kecil, ukuran partikel yang lebih kecil, dan viskositas yang lebih tinggi.
4. Kesimpulan
(1) Semakin tinggi kandungan padatan emulsi, semakin besar viskositasnya.
(2) Semakin tinggi derajat polimerisasi koloid pelindung PVA, semakin besar viskositas emulsi, dan sebaliknya.
(3) Viskositas emulsi ketika PVA digunakan sebagai koloid pelindung lebih tinggi dibandingkan ketika selulosa atau surfaktan digunakan sebagai koloid pelindung.
(4) Dengan derajat polimerisasi yang sama, semakin tinggi derajat alkoholisis, semakin rendah viskositas emulsi.
(5) Semakin banyak inisiator awal dan jumlah total inisiator yang ditambahkan, semakin tinggi viskositas emulsi.
Situs web: www.elephchem.com
WhatsApp: (+)86 13851435272
Surel: admin@elephchem.com